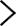A contact lens-induced peripheral ulcer (CLPU) is when the contact lens becomes contaminated with harmful bacteria like Staphylococcus. This usually happens on one side and is more common in people wearing extended contact lenses. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of CLPU, its causes, symptoms, treatment options and preventive measures, ensuring optimal eye health for contact lens wearers.
What is a contact lens-induced peripheral ulcer?
A contact lens-induced peripheral ulcer (CLPU) usually happens in one eye. It occurs when gram-positive bacteria, especially Staphylococcus Aureus, stick to the contact lens and release harmful substances called exotoxins. The immune system of the person wearing contact lenses doesn’t recognise the foreign substance, leading to a corneal ulcer.
What causes contact lens-induced peripheral ulcer?
A lens-induced peripheral ulcer can be caused by:
- Bacterial contamination
- Tight-fitting contact lenses
- Poor lens hygiene practices
Risks associated with CLPU
Contact lens wearers should be aware of the following risk factors associated with CLPU:
- Individuals with high ametropia (>5D) are more susceptible to CLPU
- Teenagers and young adults aged 15-25 are more at risk
- Contaminated lens cases increase the risk of CLPU
- Environmental changes
Signs and symptoms of peripheral ulcer for contact lens wearers
The following signs and symptoms may be an indication of a lens-induced peripheral ulcer:
- Unfamiliar body sensation
- Light sensitivity (photophobia)
- Watery eyes
- Red eyes
- Discomfort in eyes
If you think you might have a CLPU, you must seek advice from your optician or nearest eye casualty department immediately. Corneal ulcers can damage your vision permanently and lead to blindness if left untreated.
How do you treat a contact lens-induced corneal ulcer?
Contact lens-induced corneal ulcer usually starts to improve within a couple of days after discontinuing lens usage but can vary depending on the cause of the ulcer. Your eye healthcare provider might suggest antibiotic eye drops for bacterial infection and hydrating eye drops to keep your eyes lubricated.
If left untreated, corneal ulcers can also lead to severe eye problems. Therefore, you should consult an eye care professional to treat this condition.
How do you prevent corneal ulcers for contact lens wearers?
Contact lens wearers can prevent corneal ulcers by:
- Maintaining proper eyelid hygiene
- Washing and drying hands thoroughly before touching your eyes and contact lenses
- Giving the eyes a break from contact lenses when possible
- Following the advice of an optician regarding lens-wearing time
- Opting for daily disposables as a new pair every day reduces the risk of infection
- Avoiding dust, pollen, smoke and allergens
If you face unusual symptoms even after following these preventive methods, i.e. discomfort in your eyes, bloodshot eyes or a burning sensation while wearing contact lenses, you should remove your lenses immediately. If the symptoms persist, contact your eye doctor as soon as possible.
Disclaimer: The advice in this article is for informational purposes only and does not replace medical care or an in-person check-up. Please check with an eyecare professional before purchasing any products or remedies. For information on our article review process, please refer to our Editorial Policy.

 Offers
Offers Account
Account
 Favorite
Favorite
 Basket
Basket

 OFFERS
OFFERS