Medically reviewed by Khuram Sarwar, Dispensing Optician at Feel Good Contacts.
Albinism is a rare genetic condition that affects the production of melanin, a kind of pigmentation that determines the colour of the skin, hair and eyes. This is the reason why albino people generally have pale skin tone. Melanin also plays a role in maintaining the health of the optic nerve. They are also prone to the risk of vision loss. Male or female, anyone can be born with this condition. In this article, we will delve into the complexities around albinism, providing insights into its intricacies, underlying causes, far-reaching effects on individuals and the essential resources available to those suffering from this condition.
What is albinism?
Albinism is a rare genetic condition in which the pigment responsible for colouring eyes, skin and hair stops producing melanin. People suffering from albinism define themselves as "Albino", derived from the Latin word "Albus", meaning white, implying that people suffering from albinism generally have pale or whitish skin and brown hair.
Albinos also have a high risk of skin cancer in the early years of their lives. This is because of lack of melanin, whose basic function is to shield the skin from the sun's harmful UV rays, making their skin prone to sunburns. Furthermore, lack of melanin can disrupt the seamless vision capabilities of a person.
Albinism is a rarely occurring genetic condition in people across the world, no matter what their gender is, where they come from, their race, ethnicity, and sexuality. In the UK, almost 1:17,000 people suffer from this life-long condition . Not a contagious disease, albinism is a hereditary condition, meaning people are born with it. Although this condition doesn't have a cure, with proper mitigation strategies, one can implement certain coping mechanisms.
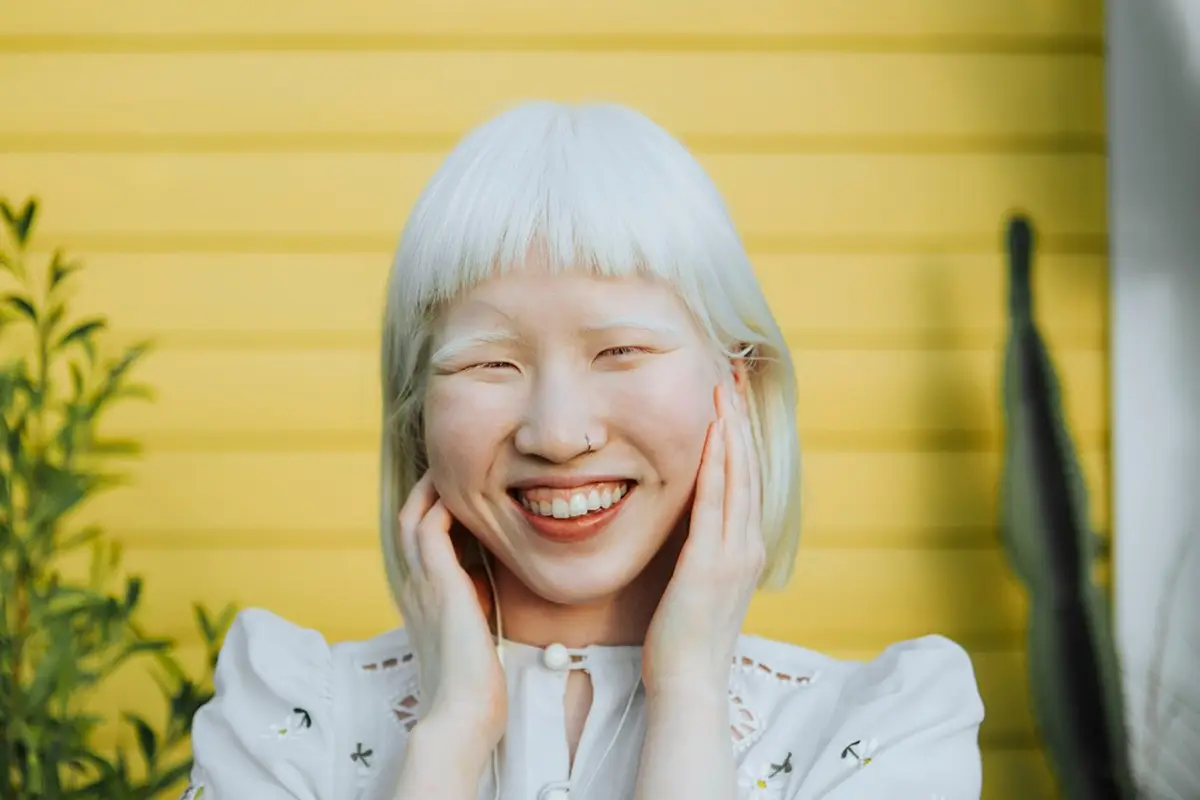

What causes albinism?
Albinism is a condition that occurs when specific genes (melanocytes) responsible for producing and distributing melanin are defective, impacting a person’s vision. This condition typically occurs when both parents carry the genes for albinism, causing a lack of melanin or minimal production. When these genes are changed, it can result in either an absence or a decrease in melanin production. Medical professionals estimate that 1:70 of the population bears these genes.
Genetic variations can lead to various forms of albinism affecting the melanin level of skin, hair and eyes.
What are the four types of albinism?
Albinism is segregated into four different types.
- Oculocutaneous Albinism (OCA): regarded as the most common type of albinism, this is known to affect the skin, hair and eyes due to low melanin production. Medical specialists have further categorised this albinism from OCA1 to OCA7 due to autosomal recessive inheritance. In this condition, the offspring inherits two copies of the changed gene from each parent. Each OCA type has its unique attribute depending upon its gene mutation. OCA1 and OCA2 are the most commonly occurring albinisms; almost 2:80,000 people suffer from these subtypes. Their skin appears to be white and pale in most cases. People with OCA3 generally have brown skin, hair and eye problems. OCA4 has similar attributes to that of OCA2. The remaining subtypes are the rarest occurring albinism in the world.
- Ocular Albinism: mainly found in males due to the mutation of genes in the X-chromosome; this condition affects the vision of a person, reducing the colour of the retina and iris. The skin and hair remain unaffected. It is a rarely occurring condition in comparison to OCA.
- Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome (HPS): this is a much rare variant of albinism and is prevalent in Puerto Rico. The symptoms are similar to OCA, however, it can also cause bowel syndrome, bleeding disorders and issues with the lungs and kidneys.
- Chediak-Higashi syndrome (CHS): one of the rarest forms of albinism occurring in less than 500 people worldwide. Although the symptoms are similar to OCA, it doesn't affect the skin completely. In this case, the skin has a greyish shade, with blonde hair and silver streaks. People with CHS are generally susceptible to infections due to defective white blood cells and immune and neurological problems.
What are three symptoms of albinism?
The primary symptoms of albinism are recognised in the attributes of skin, hair and eyes. Below are some of the symptoms of albinism:
Skin
Lighter skin tones can lead to a burning sensation from sun exposure and develop freckles, pink moles and lentigines on the skin.
Hair Colour
Although the hair colour changes from white to brown, the colours tend to darken as the affected person ages.
Eye Colour
The eye colour tends to change from light blue to shades of brown. The iris becomes sensitive to light due to its inability to protect from the sun's harmful rays. It might appear translucent or red due to low melanin levels.
People coping with albinism often suffer from vision problems, including Strabismus (crossed eyes or walleye), extreme level of myopia (near-sightedness) and hyperopia (farsightedness). Due to underdeveloped optic nerve, people with albinism are visually impaired or have blurred vision.
Is there a cure for albinism?
There is no cure for albinism, but proper mitigation strategies can help alleviate symptoms of the condition to worsen further.
- UV-protected sunglasses can be worn to protect eyes from the harmful UV rays of the sun.
- Protect your skin by applying a high-SPF sunscreen. To ensure extra protection from the sun, you can also wear a hat.
- Wearing prescription glasses helps in the clarity of vision.
- Regular eye tests need to be conducted to regulate vision-related issues.
- Corrective surgery on eye muscles is another option for those who experience eye alignment issues.
What are the best resources and organisations for more information about albinism?
People with albinism can cope with this condition from verified resources and support organisations:
- The Albinism Fellowship UK is a registered volunteer-led organisation that provides valuable information, advice, and support for albino people and their families.
- The Global Albinism Alliance facilitates relevant resources and skill development programmes for albinism groups across the globe. It encourages participation among albinism groups and stakeholders to amplify their voices at a global level.
- Living with conditions like albinism isn’t an obstacle to working in a corporate environment. The Equality Act enables employers to make reasonable modifications to support people with disabilities like albinism, such as a hybrid work scheme, allowance for regular medical check-ups, a vibrant work environment, etc.
- Access to work is a government-initiated scheme that grants employers with specific disabilities the resources required for employment.
How do people with albinism feel?
Twenty-two-year-old Leo and his sister, who have been battling albinism, initially struggled to accept this condition. Later, Leo became proud of his unique features and now works as a professional model. Leo’s life is a source of inspiration to albino people with dreams.

 Offers
Offers Account
Account
 Favorite
Favorite
 Basket
Basket

 OFFERS
OFFERS